Electrical stimulation can be used for a variety of therapeutic purposes, depending on your condition and treatment goals. Here are some common reasons why a physical therapist might use electrical stimulation:
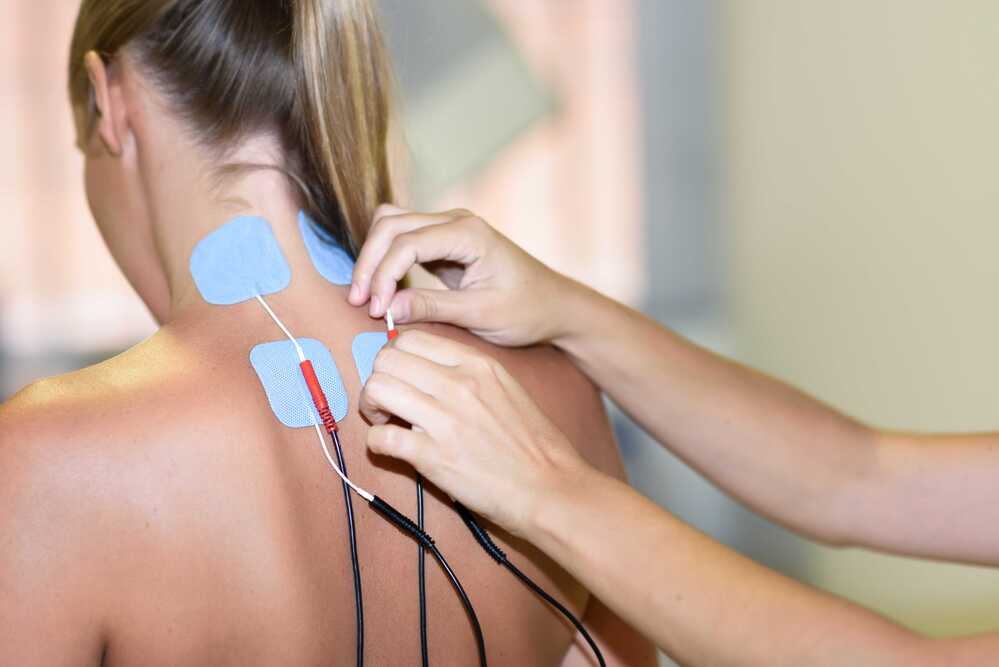
Electrical stimulation can help reduce pain, particularly for acute or chronic pain conditions. It works by interfering with the transmission of pain signals to the brain, providing pain relief.
Electrical stimulation can be used to activate and strengthen muscles, making it beneficial for patients who have muscle weakness or difficulty moving certain muscle groups due to injury, surgery, or neurological conditions.
Patients who are unable to use or move their muscles for extended periods, such as after surgery or due to immobilization, can experience muscle atrophy (muscle wasting). Electrical stimulation helps prevent or slow down muscle loss by contracting the muscles.
In cases of neurological conditions or injuries, such as stroke or spinal cord injury, electrical stimulation can be used to facilitate functional movements, like walking or grasping objects. This can help patients regain independence in daily activities.
It’s important to note that the specific type of electrical stimulation and its parameters, such as the intensity and frequency, are tailored to the individual patient’s condition and treatment plan. Your physical therapist will use their expertise to assess each of your needs and determine whether electrical stimulation is an appropriate and effective part of your rehabilitation program.
FREE PHONE CONSULTATION: (651) 275-4706